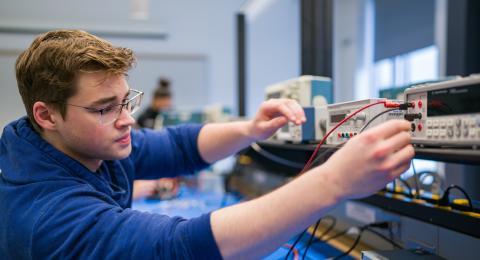
The Electrical Engineering major at UNH explores the world of power systems, circuits, and electronics, as students learn to master skills vital for shaping tomorrow. Here, you’ll study alongside engaged faculty in innovative facilities that provide students with hands-on learning experiences in an array of technical electives. You can also join one of our competition teams and choose your own senior capstone project, which helps prepare you for a career in an array of fields including telecommunications, robotics, manufacturing, aerospace and more.
What is a Bachelor of Science in electrical engineering?
This program is tailored to students who want to understand and participate in the ever-growing world of electronics technology. Students learn the fundamental concepts related to the design, development, testing and modeling of a wide range of electrical systems. By gaining skills and technological expertise, students leave this program prepared to succeed in graduate studies or a variety of career fields.
Why study electrical engineering at UNH?
You’ll work in a hands-on laboratory environment that reinforces traditional classroom learning while providing the real-world skills valued by employers. Seniors choose from a suite of professional technical electives and carry out a capstone design project tailored to their career objectives. You can complete an accelerated master’s program, participate on competitive teams at national competitions and gain real-world experience at the UNH InterOperability Lab, working alongside top tech companies to test their technologies before they hit the marketplace. This program has a high placement rate because of its great reputation among industry employers.
Potential Careers
- Advanced manufacturing
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive and Manufacturing industries
- Biomedical engineering
- Embedded computer systems
- Integrated circuits and systems design industries
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Medical IoT
- Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
- Telecommunications Industries
Curriculum & Requirements
This program is tailored to students who want to understand and participate in the ever-growing world of electronics technology. Students learn the fundamental concepts related to the design, development, testing and modeling of a wide range of electrical systems. By gaining skills and technological expertise, students leave this program prepared to succeed in graduate studies or a variety of career fields.
In addition to the university's mandatory Discovery Program requirements, degree candidates must complete our core program (freshman through junior years). In the senior year, students select professional technical electives in the areas of their interest. They also carry out a student-designed project to acquire both breadth and depth of study and to integrate knowledge across course boundaries.
For a detailed semester by semester list of requirements for the four years of study, please refer to the Degree Plan tab.
The Electrical Engineering (B Sci in Electrical Engineering) program is accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of ABET, https://www.abet.org, under the General Criteria and the Program Criteria for Electrical, Computer, Communications, Telecommunication(s) and Similarly Named Engineering Programs.
Sample Degree Plan
This sample degree plan serves as a general guide; students collaborate with their academic advisor to develop a personalized degree plan to meet their academic goals and program requirements.
| First Year | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fall | Credits | |
| ECE 401 | Perspectives in Electrical and Computer Engineering | 4 |
| MATH 425 | Calculus I | 4 |
| CS 410C | Introduction to Scientific Programming/C | 4 |
| ECON 402 or NR 411 | Principles of Economics (Micro) 1 or Environmental and Resource Economics Perspectives | 4 |
| Credits | 16 | |
| Spring | ||
| PHYS 407 | General Physics I | 4 |
| ENGL 401 | First-Year Writing | 4 |
| MATH 426 | Calculus II | 4 |
| CS 419 | Computer Science for Engineers and Scientists | 4 |
| Credits | 16 | |
| Second Year | ||
| Fall | ||
| ECE 541 | Electric Circuits | 4 |
| ECE 543 | Introduction to Digital Systems | 4 |
| PHYS 408 | General Physics II | 4 |
| MATH 527 | Differential Equations with Linear Algebra | 4 |
| Credits | 16 | |
| Spring | ||
| ECE 548 | Electronic Design I | 4 |
| ECE 562 | Computer Organization | 4 |
| MATH 645 | Linear Algebra for Applications | 4 |
| Discovery Program Category | 4 | |
| Credits | 16 | |
| Third Year | ||
| Fall | ||
| ECE 602 | Engineering Analysis | 3 |
| ECE 633 | Signals and Systems I | 3 |
| ECE 652 | Electronic Design II | 6 |
| Discovery Program Category | 4 | |
| Credits | 16 | |
| Spring | ||
| ECE 603 | Electromagnetic Fields and Waves I | 3 |
| ECE 634 | Signals and Systems II | 3 |
| ECE 647 | Random Processes and Signals in Engineering | 3 |
| ECE 653 | Electronic Design III | 6 |
| Discovery Program Category | 4 | |
| Credits | 19 | |
| Fourth Year | ||
| Fall | ||
| ECE 791 | Senior Project I 3 | 3 |
| Two Professional Electives 2 | 8 | |
| Discovery Program Category | 4 | |
| Credits | 15 | |
| Spring | ||
| ECE 792 | Senior Project II 3 | 3 |
| Two Professional Electives 2 | 8 | |
| Discovery Program Category | 4 | |
| Credits | 15 | |
| Total Credits | 129 | |
- 1
Students are required to take either ECON 402 Principles of Economics (Micro) or NR 411 Environmental and Resource Economics Perspectives to fulfill the Social Science Category of the Discovery Program.
- 2
Four professional electives must be selected as follows:
- Choose any of four ECE 700-level courses, one course could be ECE 583 Designing with Programmable Logic
- Students are allowed to take only one ECE 795 Electrical and Computer Engineering Projects or ECE 796 Special Topics
- 3
ECE 791 Senior Project I and ECE 792 Senior Project II fulfill Discovery Program Capstone Experience.
Degree Requirements
All Major, Option and Elective Requirements as indicated.
*Major GPA requirements as indicated.
Major Requirements
In addition to Discovery Program requirements, the department has a number of grade-point average and course requirements.
- Any electrical engineering major whose cumulative grade-point average in ECE courses is less than 2.0 during any three semesters will not be allowed to continue as an electrical engineering major.
- Electrical engineering majors must achieve a 2.0 grade-point average in all ECE and CS courses as a requirement for graduation.
To make an exception to any of these departmental requirements based on extenuating circumstances, students must petition the department's undergraduate committee. Mindful of these rules, students, with their advisor's assistance, should plan their programs based on the distribution of courses found in the Degree Plan tab.
Required Courses
| Code | Title | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| CS 410C | Introduction to Scientific Programming/C | 4 |
| CS 419 | Computer Science for Engineers and Scientists | 4 |
| ECE 401 | Perspectives in Electrical and Computer Engineering | 4 |
| ECE 541 | Electric Circuits | 4 |
| ECE 543 | Introduction to Digital Systems | 4 |
| ECE 548 | Electronic Design I | 4 |
| ECE 562 | Computer Organization | 4 |
| ECE 602 | Engineering Analysis | 3 |
| ECE 603 | Electromagnetic Fields and Waves I | 3 |
| ECE 633 | Signals and Systems I | 3 |
| ECE 634 | Signals and Systems II | 3 |
| ECE 647 | Random Processes and Signals in Engineering | 3 |
| ECE 652 | Electronic Design II | 6 |
| ECE 653 | Electronic Design III | 6 |
| ECON 402 | Principles of Economics (Micro) | 4 |
| or NR 411 | Environmental and Resource Economics Perspectives | |
| MATH 425 | Calculus I | 4 |
| MATH 426 | Calculus II | 4 |
| MATH 527 | Differential Equations with Linear Algebra | 4 |
| MATH 645 | Linear Algebra for Applications | 4 |
| PHYS 407 | General Physics I | 4 |
| PHYS 408 | General Physics II | 4 |
| Capstone | ||
| ECE 791 | Senior Project I | 3 |
| ECE 792 | Senior Project II | 3 |
| Professional Electives | ||
| Choose four ECE 700-level courses 1 | 16 | |
| Other Courses | ||
| Discovery requirements not already covered by required courses 2 | 24 | |
| Total Credits | 129 | |
- 1
Four professional electives must be selected as follows:
- Choose any of four ECE 700-level courses, one course could be ECE 583 Designing with Programmable Logic
- Students are allowed to take only one ECE 795 Electrical and Computer Engineering Projects or ECE 796 Special Topics
- 2
Fulfilling the EE Program curriculum taking ECE 401 Perspectives in Electrical and Computer Engineering, ECE 791 Senior Project I, and ECE 792 Senior Project II curriculum will automatically meet Discovery Category, "Environment, Technology and Society."
The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering has adopted a set of student outcomes that consists of statements describing what students are expected to know and be able to do by the time of graduation, the achievement of which indicates that the student is equipped to achieve the program objectives.
The current student outcomes are:
- An ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science, and mathematics.
- An ability to apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental and economic factors.
- An ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences.
- An ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts.
- An ability to function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives.
- An ability to develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data, and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions.
- An ability to acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
Explore Program Details
Those interested in the Electrical Engineering major may also be interested in the following advanced degrees. Students in the program also have the opportunity to participate in the UNH accelerated master’s program.
Electrical & Computer Engineering M.Eng.
Electrical & Computer Engineering M.S.
Electrical & Computer Engineering Ph.D.
Electrical & Computer Engineering: Biomedical Engineering M.S.